Workflow
The deployment workflow is illustrated by the diagram in What Is AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Why Do I Need It?:
The binding between those components is established indirectly and comprises the following activities:
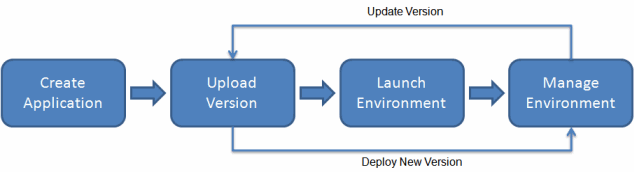
- create an application – see the Create Application action of the AWS Elastic Beanstalk Application task
- upload the application source code (the 'Source Bundle') – see the Upload File(s) action of the Amazon S3 Object task
- create an application version for that application – see the Create Application Version action of the AWS Elastic Beanstalk Application Version task
- launch an environment with one of the available application versions of an application – see the Create Environment action of the AWS Elastic Beanstalk Environment task
- manage the environment, which implies going back to 3./4. and selecting one of two approaches for deploying a new application version (be it a newly created or a former one):
update an environment
asby deploying a new application version that replaces the currently running one (usually via a rolling or immutable update), as outlined in Deploying
Versions Existing Environments by replacing the currently running application version with another one –AWS Elastic Beanstalk Environments – see the UpdateEnvironment action of the AWS Elastic Beanstalk Environment task
create a new environment, optionally swapping over to that one
by Deploying Versions with Zero Downtime once it is verified as working correctly –with zero downtime, as outlined in Blue/Green Deployments with AWS Elastic Beanstalk – see the SwapEnvironment CNAMEs action of the AWS Elastic Beanstalk Environment task
Tip title AWS demotes CNAME swap If your application architecture and deployment scenario allow to use rolling or immutable updates, AWS nowadays recommends these more flexible approaches over a CNAME swap – refer to table Deployment Methods within Deploying Applications to AWS Elastic Beanstalk Environments for a comparison of available deployment methods.
Alternative workflow via CloudFormation
As an alternative to using the AWS Elastic Beanstalk tasks built into Tasks for AWS, it is also possible to provision the Elastic Beanstalk components directly via the AWS CloudFormation Stack task and the corresponding CloudFormation resource types:
A typical workflow based on CloudFormation might look as follows:
- upload the application source code (the 'Source Bundle') – see the Upload File(s) action of the Amazon S3 Object task
- create/update the CloudFormation stack that provisions the Elastic Beanstalk application, application version and environment – see the Create Stack action of the AWS CloudFormation Stack task
 You can use the Update stack, if it already exists option to reuse the same Bamboo job for both actions
You can use the Update stack, if it already exists option to reuse the same Bamboo job for both actions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
| Questionslist macro | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|